VBA OBJECTS
Microsoft Office has quite large built-in VBA library.
If we writing a code in Excel, we can switch on F2(or Fn + F2) on the keyboard to see the Object Browser as also we can go to View in VBA and choose Object Browser from the list (screen below). Most defined classes are focused on Application, Sheets, Workbooks, Ranges, Tables and Charts. Today I will show you some examples for some of them.

OBJECT:APPLICATION
Application is an option if we want to make some basic moves in Excel, like open new Wrokbbok, Close Apps, Delete some rows or column form App level.
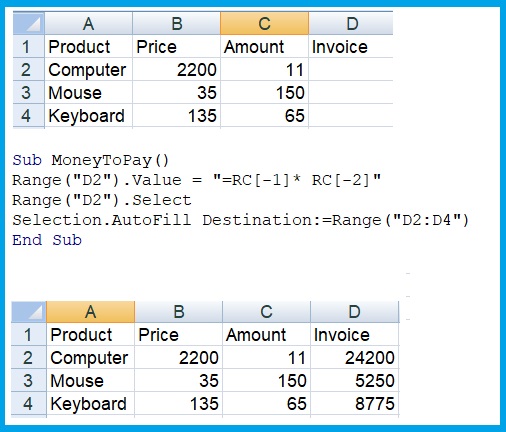
Sub ApplicationObject()
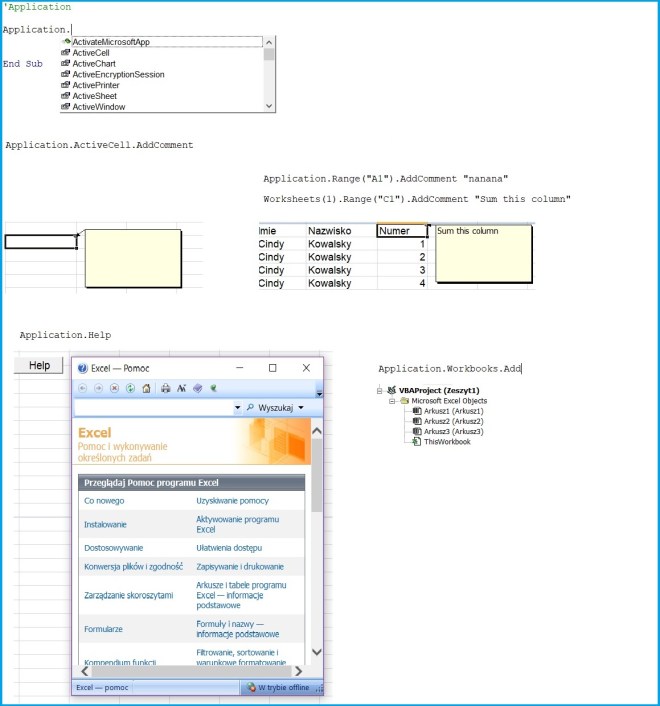
Application.ActiveCell.AddComment “sum this column”
Application.Range(“A1”).AddComment “example”
Application.Help
Application.Workbooks.Add
Application.Workbooks.Close
Application.Rows.Delete
Application.Range(“B2”).Delete
Application.Quit
End Sub
OBJECT WORKBOOOK
Then we can focus on a simple workbook at make some moves from this side, for example create a password, locked ranges from editing, save our workbooks and close them.
Sub WorkBookObject()
ActiveWorkbook.Protect “nanana”, True, True
ActiveWorkbook.Protect Password:=”nanana”, Structure:=True, Windows:=True
ActiveWorkbook.Save
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=”C:\Users\aszcz\desktop\test.xlsm”
ActiveWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=”C:\Users\aszcz\desktop\test2.txt”
ActiveWorkbook.RefreshAll
ActiveWorkbook.Close
End Sub
OBJECT SHEET
Look like an inception the way we’re going down with this object :), now let’s try some ecamples with simple Sheets:
Sub WorksheetObject()
Worksheets.Add
Worksheets(1).Copy
Worksheets(1).Select
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Select
ActiveSheet.SaveAs Filename:=”C:\Users\aszcz\desktop\test3.xlsm”
End Sub
OBJECT RANGE
Today’s post will be finished with codes examples showing some useful tips for ranges management.
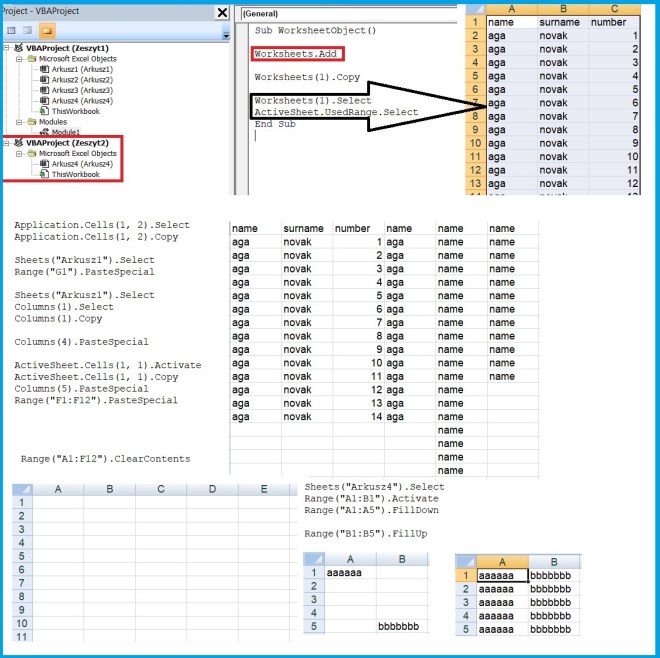
Sub RangeObject()
Range(“A1”).Select
Range(“A2”).Copy
Sheets(“Arkusz2”).Select
Range(“A1”).PasteSpecial
Application.Cells(1, 2).Select
Application.Cells(1, 2).Copy
Sheets(“Arkusz1”).Select
Range(“G1”).PasteSpecial
Sheets(“Arkusz1”).Select
Columns(1).Select
Columns(1).Copy
Columns(4).PasteSpecial
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 1).Activate
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 1).Copy
Columns(5).PasteSpecial
Range(“F1:F12”).PasteSpecial
Range(“A1:F12”).ClearContents
Range(“F1:F15”).ClearFormats
Sheets(“Arkusz1”).Select
Range(“A1:C1”).Delete
Worksheets(“Arkusz3”).Range(“A1”).Consolidate _
Sources:=Array(“Arkusz1!R1C1:R37C6”, “Arkusz2!R1C1:R37C6”), _
Function:=xlSum
Sheets(“Arkusz1”).Select
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.Select
Sheets(“Arkusz4”).Select
Range(“A1:B1”).Activate
Range(“A1:A5”).FillDown
Range(“B1:B5”).FillUp
End Sub
The more examples you will make by your own the better knowledge you will posses.
All objects are defined systematically at docs.microsoft.com.
And little useful simple code at the end of this post