Transact SQL is an extenstion for SQL language and allow us to create variables, loops, own functions or conditional statements.
If you have some experience with VBA this examples will looks quite familiar for you.
First of all we should learn how to define a variable in SQL.
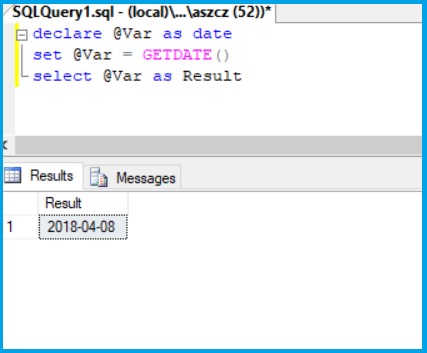
Example 1
declare @Var as date
set @Var = GETDATE()
select @Var as Result
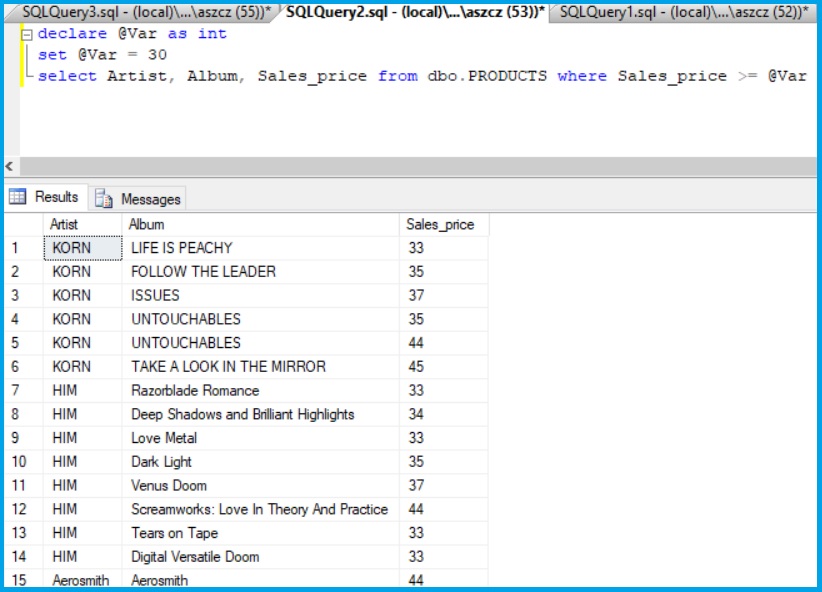
Example 2
declare @Var as int
set @Var = 30
select Artist, Album, Sales_price from dbo.PRODUCTS
where Sales_price >= @Var
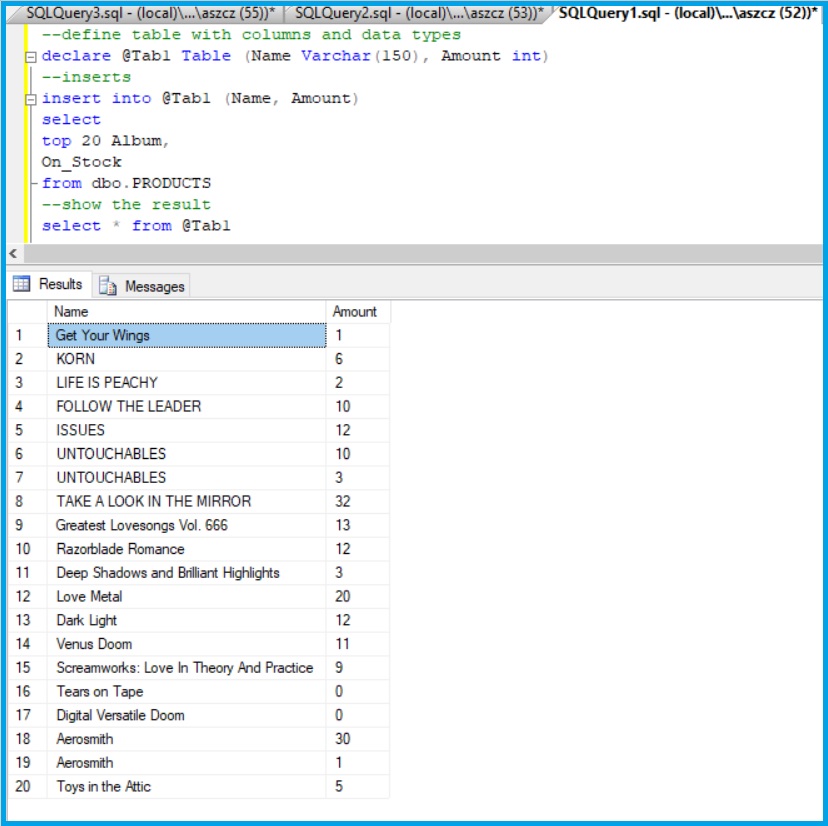
T-SQL is useful if we want to define not only one variable but even whole tables
Example 3
--define table with columns and data types
declare @Tab1 Table (Name Varchar(150), Amount int)
--inserts
insert into @Tab1 (Name, Amount)
select
top 20 Album,
On_Stock
from dbo.PRODUCTS
--show the result
select * from @Tab1
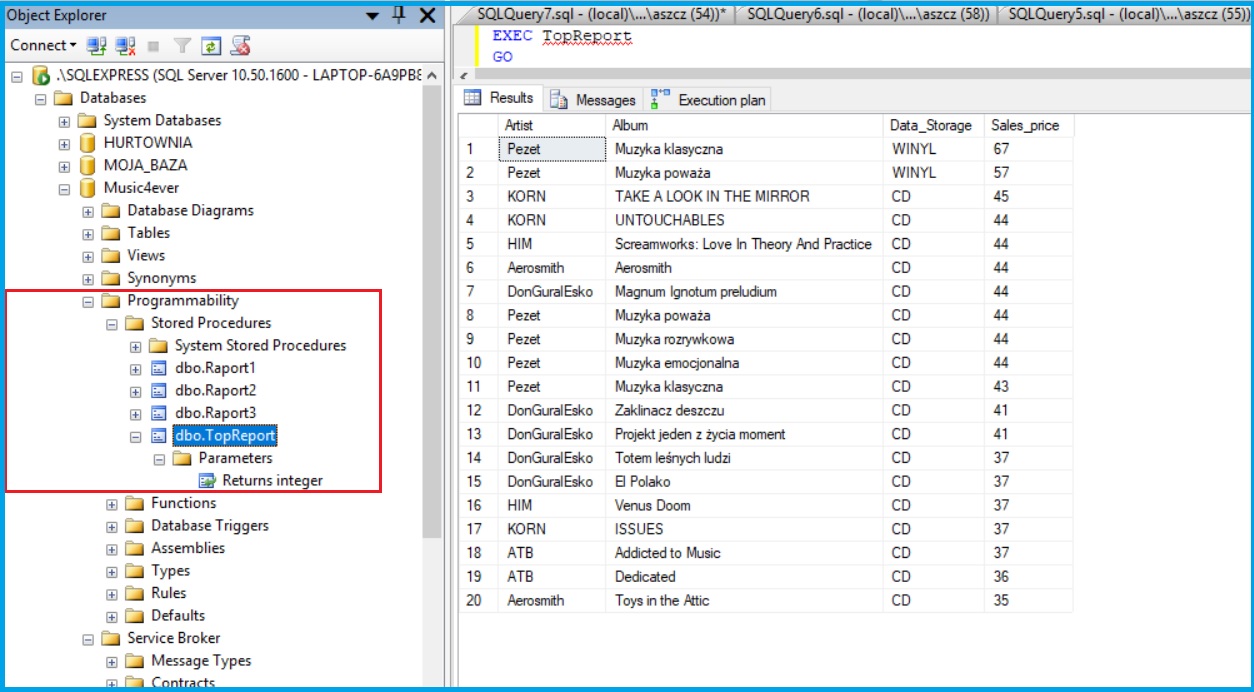
Procedures
Example 4
Create Procedure TopReport
AS
BEGIN
SELECT top 20 Artist, Album, Data_Storage, Sales_price from dbo.PRODUCTS
Where Condition = 'New'
order by Sales_price desc
END
then use:
EXEC TopReport
GO
result:
Example 5
with [basic] aggregating function like ‘count’
Create Procedure CountReport
AS
BEGIN
SELECT COUNT (Sales_price) as HowMany from dbo.PRODUCTS
Where Sales_price >= 18
END