Exercises on ready-made datasets available in Python libraries such as scikit learn or seaborn are more enjoyable the better we understand the data we are working with. I made some examples with the dataset I have chosen for today’s lesson.
dataset: taxis
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Load the "taxis" dataset
taxis = sns.load_dataset('taxis')
# Display basic information about the dataset
print(taxis.info())
# Display summary statistics
print(taxis.describe())
# Check for missing values
print(taxis.isna().sum())
# Replace missing values with zeros
taxis_filled = taxis.fillna(0)
# Verify that there are no more missing values
print(taxis_filled.isna().sum())
# Plot the distribution of fares
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
sns.histplot(taxis_filled['fare'], bins=30, kde=True)
plt.title('Distribution of Taxi Fares')
plt.xlabel('Fare')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.show()

# Calculate the average fare by passenger count
average_fare_by_passenger =
taxis.groupby('passengers').fare.mean().reset_index()
# Bar plot of average fare by passenger count
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.bar(average_fare_by_passenger['passengers'],
average_fare_by_passenger['fare'], color='violet')
plt.title('Average Fare by Passenger Count')
plt.xlabel('Number of Passengers')
plt.ylabel('Average Fare ($)')
plt.xticks(average_fare_by_passenger['passengers'])
plt.grid(False)
plt.show()
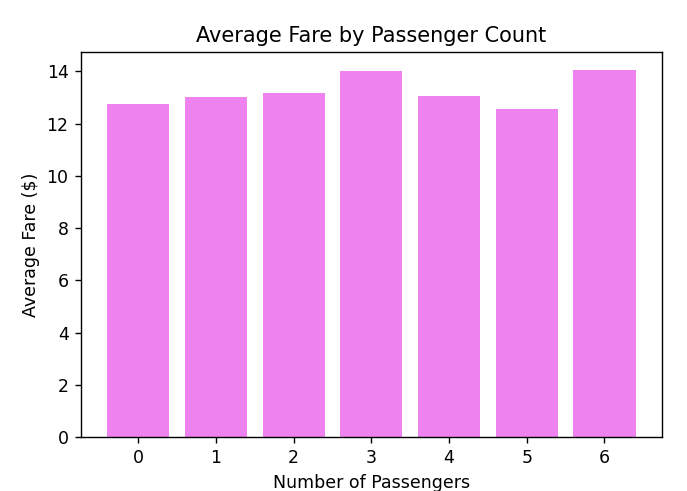
dataset: diamonds
diamonds = sns.load_dataset('diamonds')
# Display basic information about the dataset
print(diamonds.info())
# Display summary statistics
print(diamonds.describe())
# Display the first few rows of the dataset
print(diamonds.head())
#Display first and last rows as common result
print(pd.concat([diamonds.head(), diamonds.tail()])
# Count the number of rows in the dataset
num_rows = diamonds.shape[0]
print(f"The number of rows in the diamonds dataset is: {num_rows}")
# List the name of headers
for headers in diamonds.columns:
print(headers)
# Select data from diamonds dataset:
#5 selected columns and 1000 rows + headers
diamonds_data = diamonds[['carat', 'cut', 'color',
'clarity', 'price']].head(1001)
# Show selected data
print(diamonds_data)
# or as dataset with pandas
df_diamonds_data = pd.DataFrame(data=diamonds_data)
print(df_diamonds_data)
ops on diamonds: count, drop column, pivot table
# Count how many Ideal score is in column cut
print(df_diamonds_data['cut'].value_counts()['Ideal'])
# Drop one column in dataset
df_diamonds_data.drop('clarity',
axis=1,
inplace= True)
print(df_diamonds_data)
# Create pivot table
table = pd.pivot_table(df_diamonds_data,
values=['color', 'cut'],
index=['carat', 'price'],
aggfunc={'carat': "mean",
'price': ["min", "max", "mean"]})
print(table)