OS implements some useful functions on pathnames. Path parameters can be passed as either strings, or bytes. Applications are encouraged to represent file names as (Unicode) character strings.
import os
#The function returns a tuple of data retrieved from the csv file
def get_data(csv_file):
data = [] # declare an empty list for data from a file
if os.path.isfile(csv_file): # file source verification
with open(csv_file, "r") as content: # open 4 read
for lines in content:
lines = lines.replace("\n", "")
lines = lines.replace("\r", "") # remove line breaks
# adding items to the stamp and the stamp to the list
data.append(tuple(lines.split(",")))
else:
print ("Chosen file", csv_file, "does not exist!")
return tuple(data) # transform the list into a tuple and return it
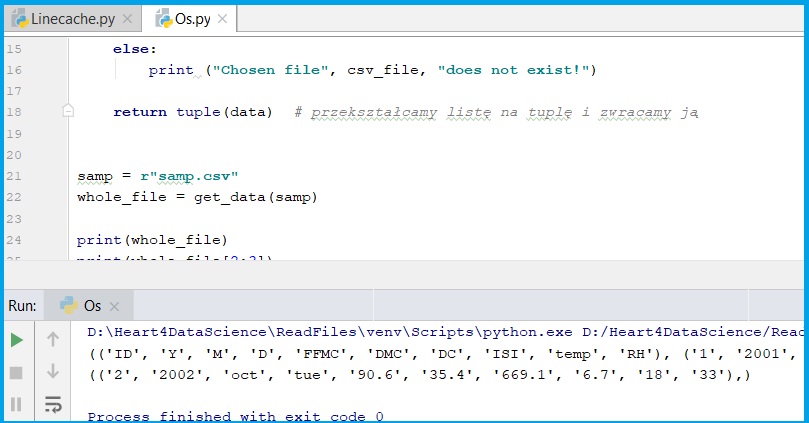
samp = r"samp.csv"
whole_file = get_data(samp)
print(whole_file)
print(whole_file[2:3])
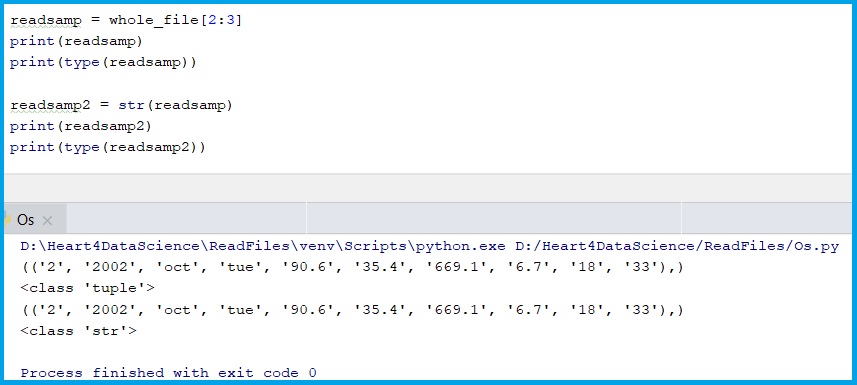
readsamp = whole_file[2:3]
print(readsamp)
print(type(readsamp))
readsamp2 = str(readsamp)
print(readsamp2)
print(type(readsamp2))
#saving data to a new csv file
plik = open("samp2.csv", "w")
plik.write(readsamp2)
plik.close
# change the content
sourcefile = open(samp).readlines()
destinyline = open(samp, "w")
for x in sourcefile:
destinyline.write(x.replace("X", "Y"))
destinyline.close()