RANGE
is used to generate a sequence of numbers according to given parameters. Really seful in loops declarations, lists or sets of numbers.
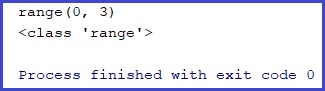
nums1 = range(3)
print(nums1)
print(type(nums1))
for x in range(3):
print(x)
for x in range(1,4):
print(x)

nums2 = range(1,10,2)
for x in nums2:
print(x)
nums3 = list(nums2)
print(nums3)
nums2 = list(range(10))
print(nums2)
IF STATEMENTS
Simple expressions
if expr1 < expr4:
print("ok")
if expr1 % 2 == 0:
print(expr1,"is disivible by 2")
if expr4 % 2 == 0:
print(expr4,"is even")
else:
print(expr4,"is odd")
Comparing conditions
if expr1 < int(expr3):
print(expr3,"is greater than",expr1)
elif expr1 == int(expr3):
print(expr3, "is equal", expr1)
else:
print(expr3, "is smaller than", expr1)
One line statement
#one line statement
if expr4 > int(expr3): print(expr4,"is greater than",expr3)
print(expr4) if expr4 > expr1 else print(expr1)

LOOPS
While Loop
# WHILE simple one
x = 0
while x < 4:
print(x)
x += 1
#output: 1 2 3
# WHILE with BREAK
x = 0
while x >= 0:
print(x)
if x == 10:
break
x += 1 #output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
x = 0
while x >= 0:
print(x+2)
if x == 10:
break
x += 1 #output: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
x = 0
while x >= 0:
print(x)
if x == 10:
break
x += 2 #output: 0 2 4 6 8 10
# WHILE YIELD in range def as function
#1)
def xRange(start, stop, step):
i = start
while i < stop:
yield i
i += step
for i in xRange(0.0, 0.3, 0.1):
print(i) # output: 0.0 0.1 0.2
#2)
def xRange(start,stop, step):
i = start
while i < stop:
yield i
i += step + 2
for x in xRange (0,10,2):
print(x) # output: 0 4 8
For Loop
#FOR simple one
words = ["Love", "Music", "Passion"]
for x in words:
if x == "Love":
continue
print(x)

#FOR in range with decimal example
from decimal import *
for i in xRange(0.0, 0.3, 0.1):
print(Decimal(i))
#statements
print((0.1 + 0.2) == 0.3)
print(round((0.1 + 0.2), 2) == round(0.3, 2))
print((Decimal(0.1) + Decimal(0.2)) == Decimal(0.3))
print((Decimal('0.1') + Decimal('0.2')) == Decimal('0.3'))
COMPREHENTIONS
# lists comprehensions
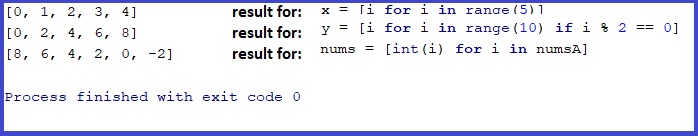
x = [i for i in range(5)]
print(x)
y = [i for i in range(10) if i % 2 == 0]
print(y)
# numbers as characters
numsA = ["8", "6", "4", "2", "0","-2"]
nums = [int(i) for i in numsA]
print(nums)
# with statement
L1 = [1,4,3,2,0,6,5,7,8,9
n = [i > 5 for i in L1]
print(n)
#output:
#[False, False, False, False, False, True, False, True, True, True]
# mix - error!
numsB = ["a", "6", "b", "2"]
nums = [int(i) for i in numsB]
print(nums)

vec_of_vec = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
single = [num for elem in vec_of_vec for num in elem]
print(single)
# dict comprehensions - reverse the order
Dict1 = {1: "Green", 2: "Yellow", 3: "Orange"}
print({value: key for key, value in Dict1.items()})
# comprehensions in sets
List1 = [1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 5, 7, 5]
Set1 = {i for i in List1}
print(Set1)
